Rosacea: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
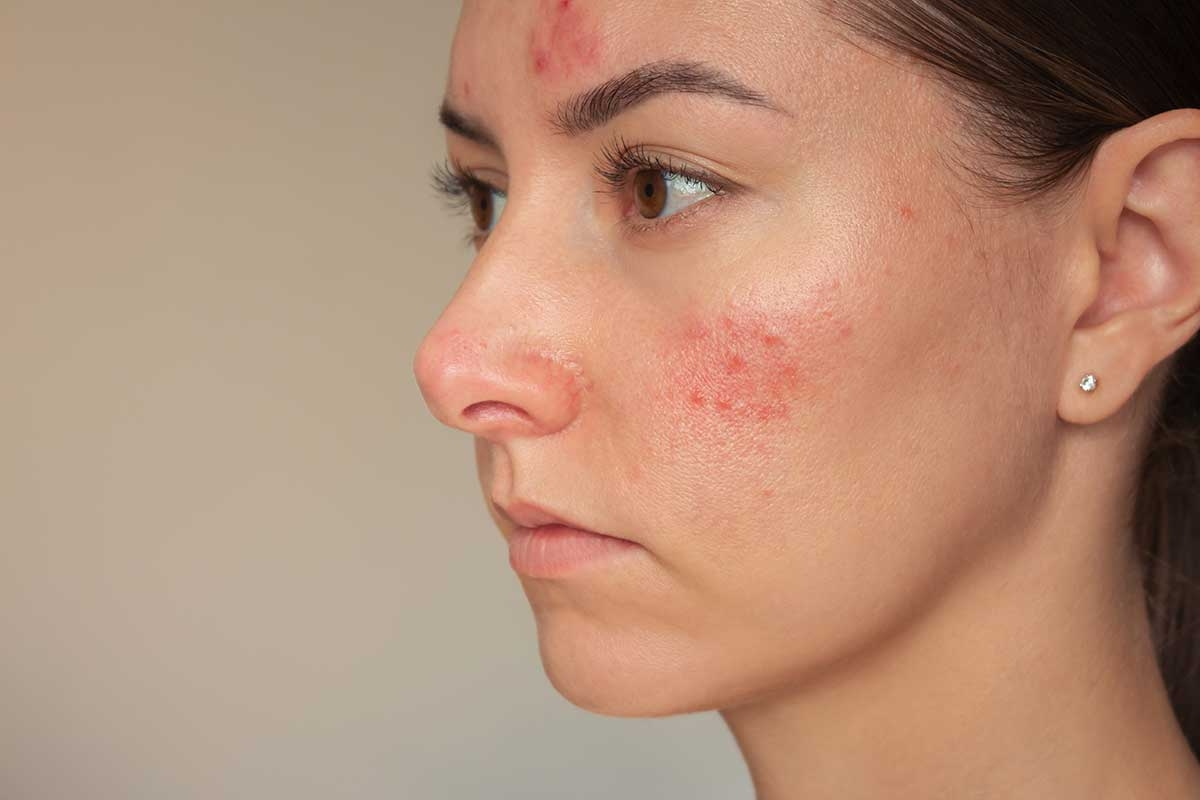
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition primarily affecting the face, marked by redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes bumps that resemble acne. While more common in women with fair skin, rosacea can affect anyone and significantly impact quality of life if left untreated. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for managing this condition effectively.
What Is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that predominantly causes persistent redness and visible blood vessels on the central areas of the face, such as the cheeks, nose, and forehead. It can also manifest in other ways, depending on the type.
Impact on Quality of Life
The visible nature of rosacea can lead to self-consciousness, anxiety, and reduced social interaction. Many individuals with rosacea report a significant impact on their emotional well-being, underscoring the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Rosacea
There are four main types of rosacea:
- Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR): Persistent redness with visible blood vessels.
- Papulopustular Rosacea: Resembles acne, with pus-filled bumps and swelling.
- Phymatous Rosacea: Thickened, bumpy skin, often affecting the nose (rhinophyma).
- Ocular Rosacea: Causes eye irritation, redness, and a gritty feeling.
Types of Rosacea
Each type of rosacea presents distinct symptoms, which may overlap in some cases.
Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR)
- Symptoms: Persistent facial redness and visible blood vessels (telangiectasia).
- Triggers: Sun exposure, alcohol, and extreme temperatures exacerbate symptoms.
Papulopustular Rosacea
- Symptoms: Redness with acne-like pustules and papules.
- Severity: Can be mistaken for acne but lacks blackheads or whiteheads common in acne.
Phymatous Rosacea
- Symptoms: Thickened skin and irregular surface texture, particularly on the nose.
- Progression: Often develops over time and is more common in men.
Ocular Rosacea
- Symptoms: Red, watery, and irritated eyes, often with a burning or gritty sensation.
- Complications: Can lead to vision problems if left untreated.
Causes of Rosacea
The exact cause of rosacea is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to its development.
Predisposing Factors
- Genetics: A family history of rosacea increases risk.
- Age and Gender: While more common in women, men are more likely to develop severe forms such as rhinophyma.
Triggers
- Environmental: Sun exposure, hot or cold weather, and wind.
- Dietary: Spicy foods, hot beverages, and alcohol are common triggers.
- Lifestyle: Stress and heavy physical exertion can exacerbate symptoms.
- Skincare Products: Certain cosmetics or harsh facial cleansers may irritate sensitive skin.
Underlying Theories
- Vascular Dysfunction: Abnormal blood vessel responses contribute to persistent redness.
- Demodex Mites: Higher levels of these microscopic mites on the skin may play a role in inflammation.
Symptoms of Rosacea
Rosacea symptoms vary by type but often include skin and eye irritation.
Primary Symptoms
- Persistent redness or flushing of the face.
- Swollen red bumps resembling acne but without comedones.
- Visible blood vessels on the cheeks and nose.
Additional Symptoms
- Burning or stinging sensations on the skin.
- Thickened skin in advanced cases, particularly on the nose.
- Eye irritation, redness, and dryness in ocular rosacea.
Diagnosing Rosacea
A thorough diagnosis helps distinguish rosacea from other skin conditions.
Clinical History
Doctors evaluate symptoms, triggers, and family history. Patients are often asked about factors that worsen their symptoms, such as sun exposure or dietary habits.
Physical Examination
The presence of persistent redness, visible vessels, or papules helps confirm the diagnosis.
Differential Diagnosis
Conditions like acne, seborrheic dermatitis, and lupus can mimic rosacea. Additional tests may be needed to rule out these conditions.
Effective Treatments for Rosacea
While rosacea cannot be cured, effective treatments are available to manage symptoms and improve skin health.
Basic Skincare Routine
- Gentle Products: Use fragrance-free, hypoallergenic cleansers and moisturizers.
- Sun Protection: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen daily to prevent flare-ups.
Topical Medications
- Metronidazole and Ivermectin: Reduce inflammation and redness.
- Azelaic Acid: Helps smooth skin texture and minimize discoloration.
Oral Medications
- Antibiotics: Low-dose doxycycline reduces inflammation in moderate to severe cases.
- Isotretinoin: Reserved for resistant cases, especially with papulopustular rosacea.
Advanced Treatments
- Laser Therapy: Reduces redness and visible blood vessels.
- Surgical Options: Corrects thickened skin in phymatous rosacea.
Lifestyle Changes
- Avoid triggers like sun exposure, spicy foods, and alcohol.
- Practice stress management techniques such as meditation or yoga.
Prevention and Control of Rosacea
Preventing flare-ups and maintaining healthy skin are key components of long-term management.
Avoid Triggers
- Identify personal triggers and adjust daily habits to minimize exposure.
- Use protective measures like sunscreen and wide-brimmed hats.
Skincare Routine
- Keep the skin hydrated and clean with gentle products.
- Avoid over-exfoliating or using harsh scrubs.
Medical Monitoring
Regular check-ups with a Dermatologist ensure treatments remain effective and address any new symptoms.
Complications Associated with Rosacea
If untreated, rosacea can lead to both physical and emotional complications.
Emotional Impact
The visible nature of rosacea can cause anxiety, depression, and reduced self-esteem, affecting social interactions and overall well-being.
Ocular Complications
Untreated ocular rosacea can result in severe dryness, corneal damage, or vision loss.
When to See a Doctor
Early consultation with a dermatologist can prevent symptoms from worsening and improve outcomes.
Key Indicators
- Persistent redness or visible blood vessels that do not improve.
- Thickened skin, especially on the nose.
- Eye irritation that impacts vision or comfort.
Conclusion
Rosacea is a chronic but manageable condition with the right approach. Early diagnosis, tailored treatments, and lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce symptoms and prevent complications.
Book an appointment with the dermatology specialists at Clinic Consultation for personalized diagnosis and effective management of rosacea.