Retinal Mapping: What Is It and What Is It For?
Vision is one of the most vital senses for humans, and taking care of our eye health is essential to maintain quality of life. One of the most important procedures for checking eye health is retinal mapping. This detailed Ophthalmological Examination allows the doctor to view a wide area of the retina, providing crucial information about eye health. In this article, we will explore what retinal mapping is, how it is performed, and what it is used for.
What Is Retinal Mapping?
Retinal mapping, also known as fundoscopy or fundus examination, is a procedure that allows the Ophthalmologist to observe the inner parts of the eye, including the retina, optic disc, macula, and blood vessels. This examination is crucial for diagnosing, monitoring, and treating conditions that affect the back of the eye. It is widely used to assess overall eye health and identify any changes that may indicate the onset of a disease.
The performance of retinal mapping is especially important for the early detection of problems that may not show immediate symptoms. By visualizing the retina and its associated structures, the ophthalmologist can detect early signs of diseases such as diabetic retinopathy or macular degeneration, allowing for early interventions that can save the patient's vision.
How Is Retinal Mapping Performed?
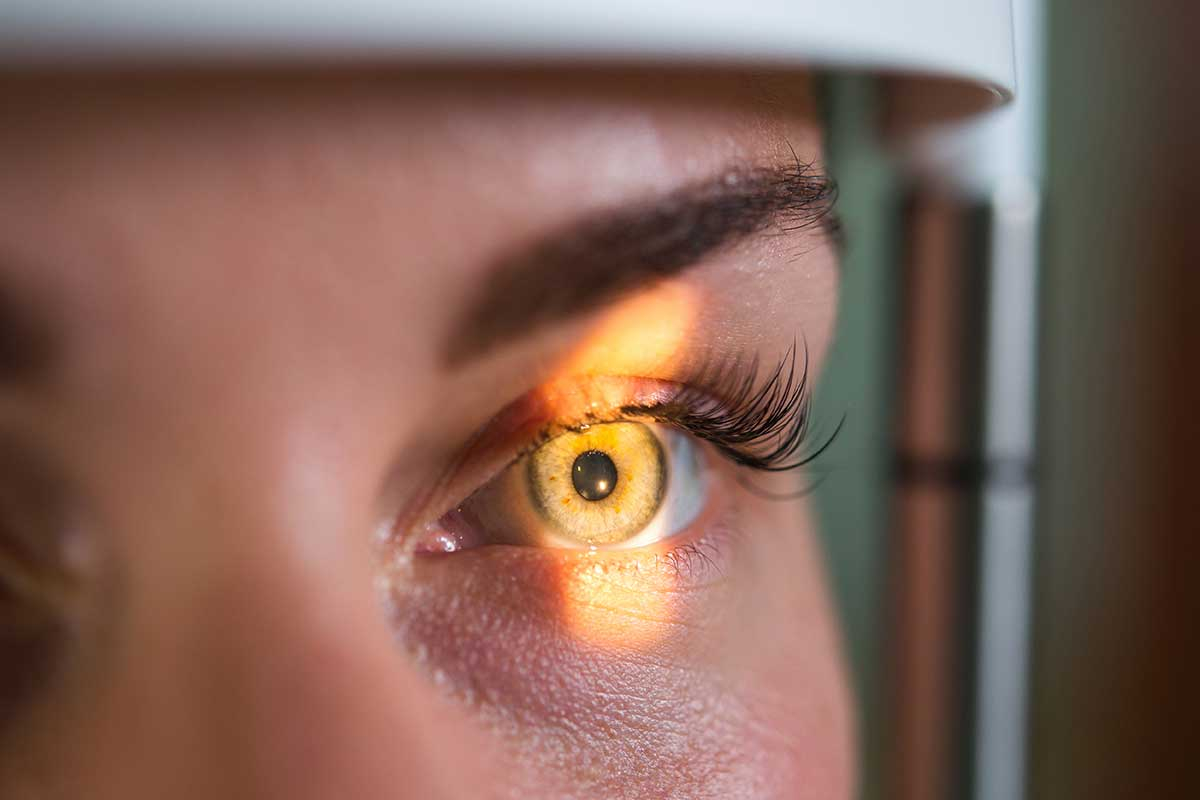
The retinal mapping exam is usually quick and painless. The patient receives eye drops to dilate the pupils, which helps the doctor get a clearer view of the inside of the eye. After dilation, which can take 20 to 30 minutes, the ophthalmologist uses an ophthalmoscope, which can be a handheld device or more sophisticated equipment coupled with a special lens, to examine the back of the eye. During the examination, the doctor may ask the patient to look in various directions to examine different parts of the retina.
Pupil dilation is an essential part of the process because it allows the doctor to have a broad and detailed view of the internal structures of the eye. Although dilation can cause light sensitivity for a few hours after the exam, this effect is temporary and considered a valid trade-off for the amount of information the exam can provide about the patient's eye health.
What Is Retinal Mapping Used For?
Diagnosis of Eye Diseases
Retinal mapping is essential for diagnosing various eye diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, retinal detachment, and glaucoma. Through this exam, changes can be detected early, allowing for more effective treatments. The exam is particularly important for identifying diseases that initially do not cause pain or any other noticeable symptoms but can lead to irreversible damage if not treated in time.
Moreover, retinal mapping helps doctors understand the stage and severity of certain eye conditions, guiding treatment decisions. For example, in the case of diabetic retinopathy, the exam can show how much the blood vessels in the retina have been affected, which is crucial for preventing the progression of the disease and vision loss.
Monitoring of Chronic Conditions
For patients with chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension, retinal mapping can help monitor the effects of these conditions on the eyes and adjust treatment as needed to prevent greater damage. This regular monitoring is vital to avoid serious complications, such as macular edema, which can lead to blindness. The exam allows the ophthalmologist to see minute changes in the retina that could indicate the need for medical interventions or adjustments in the patient's treatment regimen.
The mapping is also used to assess the effectiveness of the current treatment. If a condition is being well-managed, the exam can show stabilization or improvement of the retina's characteristics, which is a positive sign that the treatment is effective. On the other hand, if new changes are observed, this may indicate the need for adjustments in the treatment plan.
Conclusion
Retinal mapping is an indispensable tool in modern ophthalmology. It provides doctors with a detailed view of the state of eye health, enabling accurate diagnoses and timely treatment of various diseases that could otherwise lead to vision loss. Be sure to consult your ophthalmologist about the need to perform this exam as part of your regular eye health care.
FAQs
1. Is retinal mapping painful? No, the exam is painless, although the eye drops used to dilate the pupils may cause slight temporary discomfort.
2. How long does it take to perform retinal mapping? The exam itself is quick, but the preparation, including pupil dilation, can take about 30 minutes.
3. Can I drive after having retinal mapping? It is not recommended to drive immediately after the exam, as pupil dilation can temporarily affect your ability to focus and adapt to light.
4. How often should I have retinal mapping done? This depends on your risk of eye diseases and your ophthalmologist's recommendation. People at risk may need annual exams.
**5. Can retinal mapping detect problems beyond eye
diseases?** Yes, it can also help identify signs of systemic diseases, such as diabetes and hypertension, reflecting the overall health of the body.